Introduction
The evolution of automation technology has been nothing short of revolutionary, reshaping the way businesses operate and empowering organizations to streamline processes, boost productivity, and drive innovation. Among the pioneers in this digital transformation journey stands Microsoft Power Automate, a platform that has emerged as a catalyst for change in the realm of workflow automation and desktop automation. Starting from its modest origins and progressing to become a formidable force in hyper automation, Power Automate has consistently adjusted and grown to incorporate the most recent trends and breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI).
In this article, we’ll delve into the origins of Microsoft Power Automate, tracing its journey from conception to its pivotal role in today’s era of hyper automation. We’ll explore how Power Automate has embraced AI advances to empower users with intelligent automation capabilities, enabling them to tackle complex tasks with ease and efficiency.
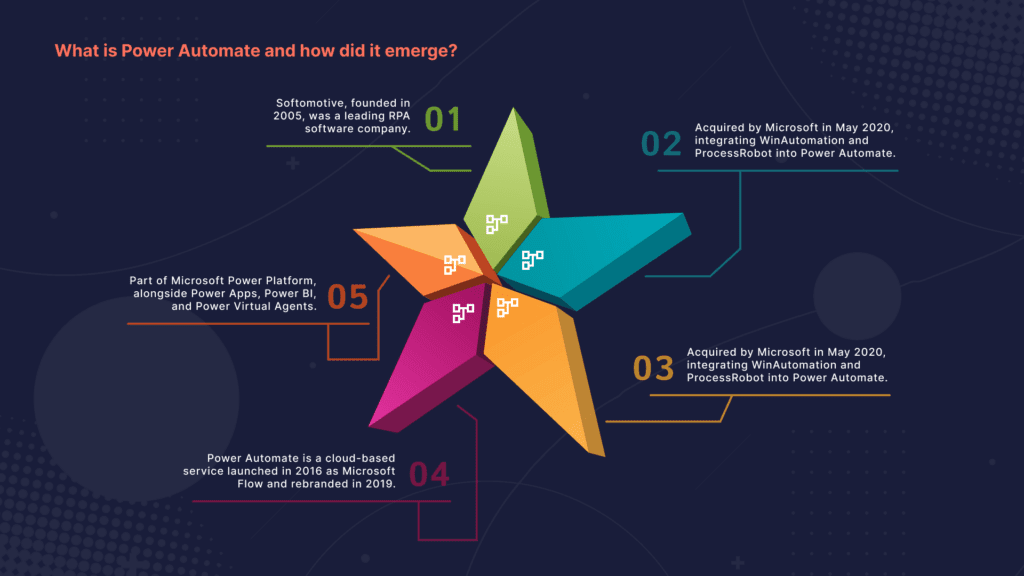
What is Power Automate and how did it emerge?
Softomotive, now part of Microsoft Power Automate, was a leading robotic process automation (RPA) software company founded in 2005. The company offered RPA solutions such as Win Automation and Process Robot, focusing on making automation accessible to a wide range of users. In May 2020, Microsoft acquired Softomotive to strengthen its RPA capabilities and integrate them into the Power Automate platform. This acquisition expanded Power Automate’s offerings with desktop automation tools and furthered Microsoft’s commitment to automation in both attended and unattended scenarios. Softomotive’s integration into Microsoft Power Automate has played a significant role in shaping the automation landscape, aligning RPA with Microsoft’s suite of productivity and cloud services.
What are some of the challenges faced in RPA CoEs and Power Automate addresses these?
While Power Automate offers significant advantages. It aims to democratize automation and empower users to automate their everyday tasks without coding. It offers a low-code graphical interface, as well as a code-first approach for advanced users. Power Automate also supports Robotic Process Automation (RPA), which enables users to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks that involve legacy systems and desktop applications.
Despite the advantages, RPA Centers of Excellence (CoEs) need to be prepared for a unique set of challenges and considerations when their support teams use this platform.
Challenges anticipated by Power Automate Users:
- Power Automate Desktop has yet to match the extensive capabilities of Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism and UiPath.
- Governance poses a challenge due to the less mature orchestration layer.
- Clarity regarding licensing remains a concern for customers.
How has RPA Adoption Landscape changed in the past 5 years?
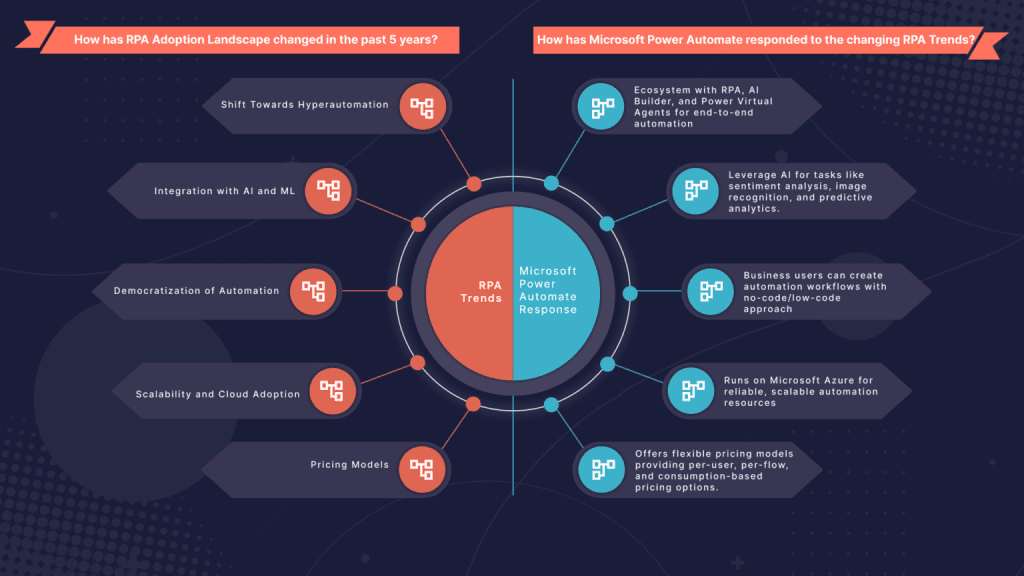
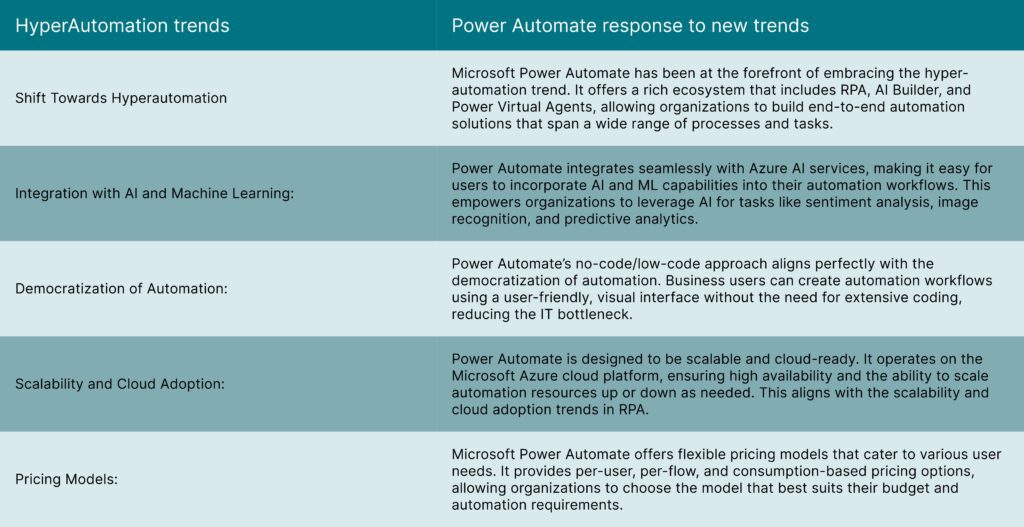
What should the RPA CoEs look out for while adopting Power Automate?
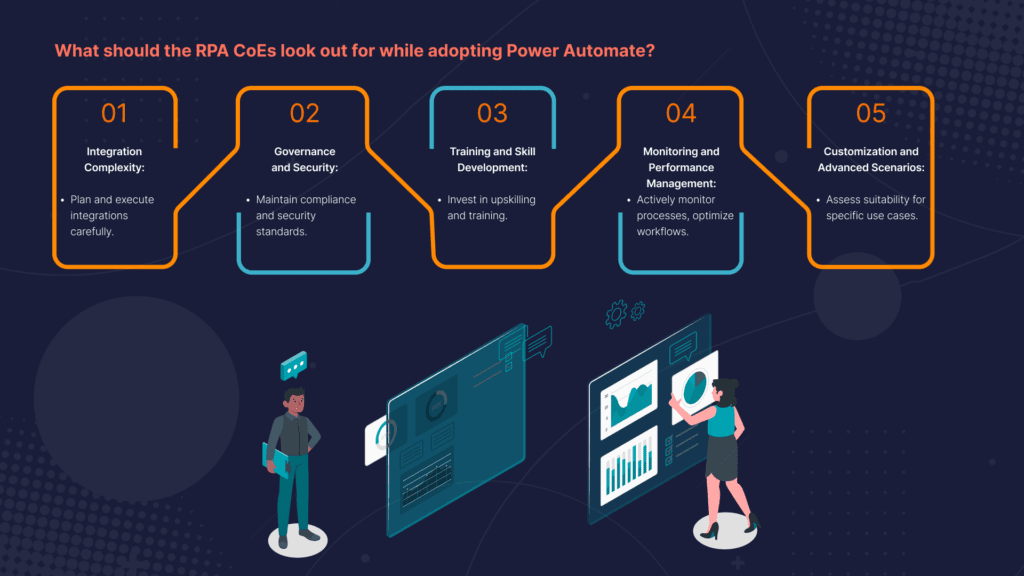
- Integration Complexity: Integrating Power Automate with existing systems and applications may be complex in certain scenarios. RPA CoEs need to carefully plan and execute integrations to ensure seamless data flow and process automation.
- Governance and Security: Maintaining governance and security standards is crucial. RPA CoEs must ensure that automation workflows adhere to compliance requirements and data security protocols, especially when handling sensitive information.
- Training and Skill Development: Transitioning to Power Automate may require upskilling and training for support teams. CoEs should invest in training resources and knowledge-sharing to empower support teams to make the most of the platform.
- Monitoring and Performance Management: Power Automate provides monitoring and performance management tools, but RPA CoEs need to actively monitor automation processes, identify bottlenecks, and optimize workflows for efficiency.
- Customization and Advanced Scenarios: Handling highly customized or advanced automation scenarios may require custom code or more advanced RPA platforms. CoEs should assess the suitability of Power Automate for specific use cases.
What are the facts and predictions of Microsoft's future plans with Power Automate success in upcoming years?
Microsoft has been investing heavily in Power Automate and its RPA capabilities, and has achieved significant success and recognition in the market. Some of the facts and predictions of Microsoft’s future plans with Power Automate success in upcoming years are:
- According to Microsoft, Power Automate has over 200,000 customers and 10 million monthly active users, and has processed over 3 billion flows per month
- According to Gartner, Microsoft is a leader in the 2020 Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms, and a visionary in the 2020 Magic Quadrant for Robotic Process Automation Software
- According to Forrester, Microsoft is a leader in the 2020 Wave for Digital Process Automation for Wide Deployments, and a strong performer in the 2020 Wave for Robotic Process Automation
- Microsoft plans to continue to expand and improve Power Automate and its RPA features, by adding more connectors, AI models, templates, and integrations with other Microsoft products and services
- Microsoft also plans to leverage its cloud, AI, and security capabilities to enable more scalable, intelligent, and secure RPA solutions for its customers
- Microsoft envisions Power Automate as a key component of its digital transformation strategy, and as a platform that can empower every person and every organization to automate their workflows and processes
Conclusion
Microsoft Power Automate has demonstrated its commitment to adapting to the recent trends in Hyper Automation and AI space and offers significant advantages for RPA CoEs. However, CoEs should be prepared for integration complexities, governance and security challenges, training and skill development needs, monitoring and performance management responsibilities, and considerations for highly customized scenarios. By addressing these challenges proactively, RPA CoEs can leverage Power Automate to empower their support teams and thrive in the era of hyperautomation, benefiting both business users and support teams.
Radium AI, a digital workforce management platform powered by Machine Learning capabilities, is revolutionizing the industry. This innovative product seamlessly integrates with major RPA platforms like UIPath, Blue Prism and Automation Anywhere, with its ongoing integration with Power Platform. Offering real-time monitoring, it serves as a centralized hub for support teams engaged in Digital Worker Management. Additionally, Radium AI boasts an array of features, such as an embedded Advanced Analytics platform and a Low-code Workflow designer for crafting new orchestrations.